Bulletproof chainmail? Next-gen fabric stiffens on demand

Bulletproof chainmail? Next-gen fabric stiffens on demand
Materials that change their properties in response to certain stimuli could come to occupy a valuable space in many fields, ranging from robotics, to medical care, to advanced aircraft. A new example of this type of shape-shifting technology is modeled on ancient chain mail armor, enabling it to swiftly switch from flexible to stiff thanks to carefully arranged interlocking particles.

Unoboxing October 6th - Ringmesh

Bulletproof Vest: Most Up-to-Date Encyclopedia, News & Reviews

NTU Singapore scientists develop fabric that can stiffen on demand

Chain Mail - an overview

Bulletproof vest - Wikipedia
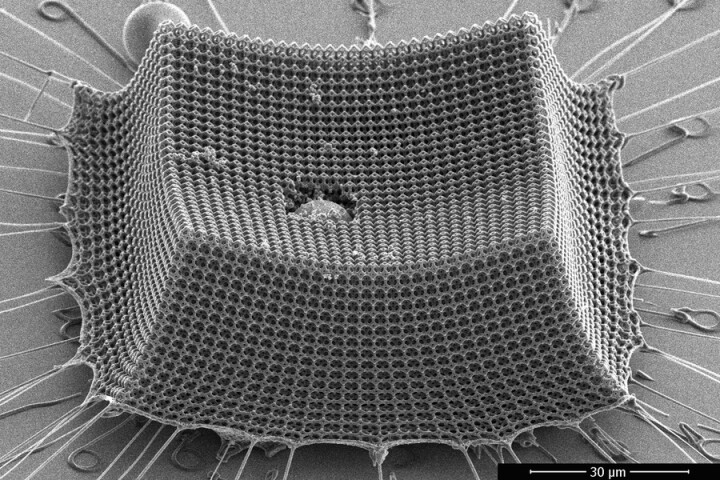
Armor
Why would anyone in the medieval era ever waste so much money on expensive full plate armor when they can simply be shot by a crossbow through that armor? - Quora
Move aside, Batman! Chain mail fabric can stiffen on demand

NTU Singapore scientists develop fabric that can stiffen on demand
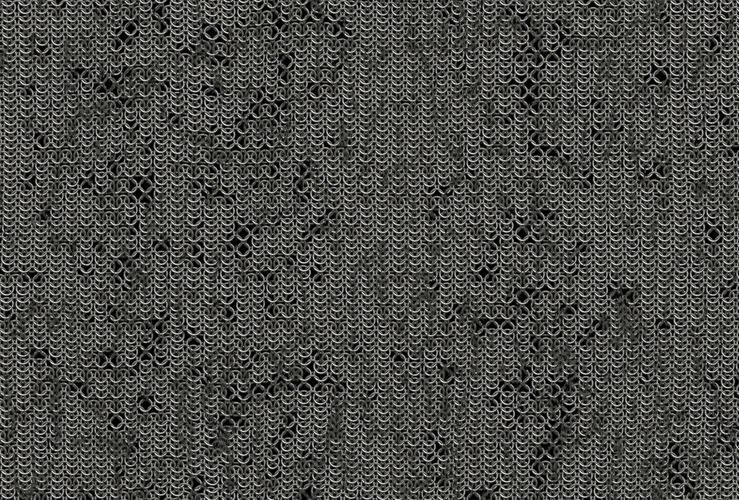
Smart Chainmail Fabric: Properties and Uses

Scientists Develop Chain Mail Fabric That Can Stiffen on Demand

Chain-mail fabric stiffens under confining pressure

Materials, manufacturing, and enablers for future soldier protection - ScienceDirect


